
Knott Laboratory provides forensic engineering and animation, Civil & Structural, and Fire & Explosion Investigation services to reconstruct accidents.
Boom Lift Operator Protection From Stored Energy Hazards
William H. Pierce, P.E. and Ben T. Railsback, M.S., P.E.
Boom lifts are useful throughout a variety of industries, such as manufacturing, maintenance service, real estate management, and construction. Boom lifts are designed to allow operator mobility at high elevations and are often used as a substitute for traditional ladders, man-baskets on lift trucks and scaffolding. Although boom lifts are very practical and efficient in allowing personnel to work at high elevations and in areas with limited access, several known hazards exist with boom lifts such as falls, machine tipping, crushes, collapse of machine and electrocution.
Although boom lift operator manuals and safety literature discuss the aforementioned hazards, they do not or incompletely discuss the hazard of suddenly released stored energy when stored energy is rapidly converted from potential energy to kinetic energy through the boom to the operator platform.
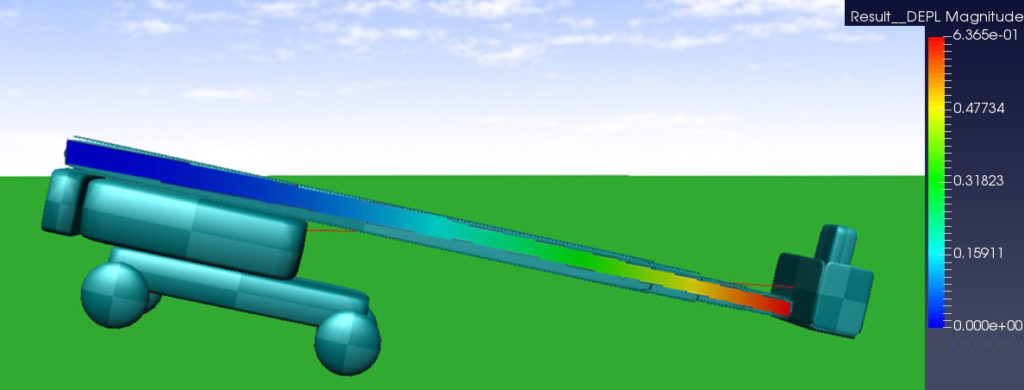
One example of rapid conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy involves the boom lift driven over a sudden drop off such as a curb. A relatively low drop off can be amplified substantially by the lever arm of the boom, and as a result, the operator platform and operator(s) within, rapidly accelerate. A second example is when the operator platform is snagged on an external structure and continued hydraulic movement builds up potential energy within the boom. The buildup of potential energy can suddenly and unexpectedly release if the platform springs free from entanglement with the structure. Such release results in the boom, the platform, and the operator(s) rapidly accelerating.
During the rapid acceleration experienced in both examples, operators can potentially be and have historically been violently thrown against the railing of the platform, ejected from the platform, and/or crushed by any nearby overhead obstacles.
The purpose of this paper is to address, analytically quantify, and propose engineering solutions to guard against the sudden conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy on boom lifts. This hazard is currently not discussed or incompletely discussed in boom lift operator manuals and safety literature.
Analytical techniques are used to quantify the rapid acceleration experienced by operator platforms and operators upon the sudden conversion of potential to kinetic energy in various scenarios. Further, the principles of safety engineering are utilized to determine methods to eliminate or reduce the frequency and severity of injuries associated with the sudden conversion of potential to kinetic energy on boom lifts.
This engineering and safety engineering analysis demonstrates that the sudden conversion of energy on boom lifts can rapidly accelerate the operator platform and operator(s) within. Further, there are technologically feasible designs that protect operators against the sudden conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy on boom lifts. Such improved, safer designs are more effective at eliminating or reducing the frequency and severity of injuries than simply warning against the hazards.
Published By
ASME 2016 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition
2016

